What Does DSG Gearbox Mean? Complete Guide to Direct Shift Gearboxes
A DSG gearbox stands for Direct-Shift Gearbox and is a type of dual-clutch automatic transmission. It uses two separate clutches to manage odd and even gears, allowing for faster and smoother gear changes without a clutch pedal. This design combines the ease of an automatic with the performance of a manual gearbox.

This system is popular in many Volkswagen Group vehicles, including Volkswagen, Audi, Skoda, and SEAT models. The dual-clutch setup lets one gear pre-select while the other is engaged, reducing shift times and improving driving efficiency.
Unlike traditional automatic gearboxes with a torque converter, the DSG avoids power loss by directly connecting the engine to the drivetrain. This makes it a technical choice for drivers who want quick shifts and a smooth ride without manually changing gears.
What Does DSG Gearbox Mean?
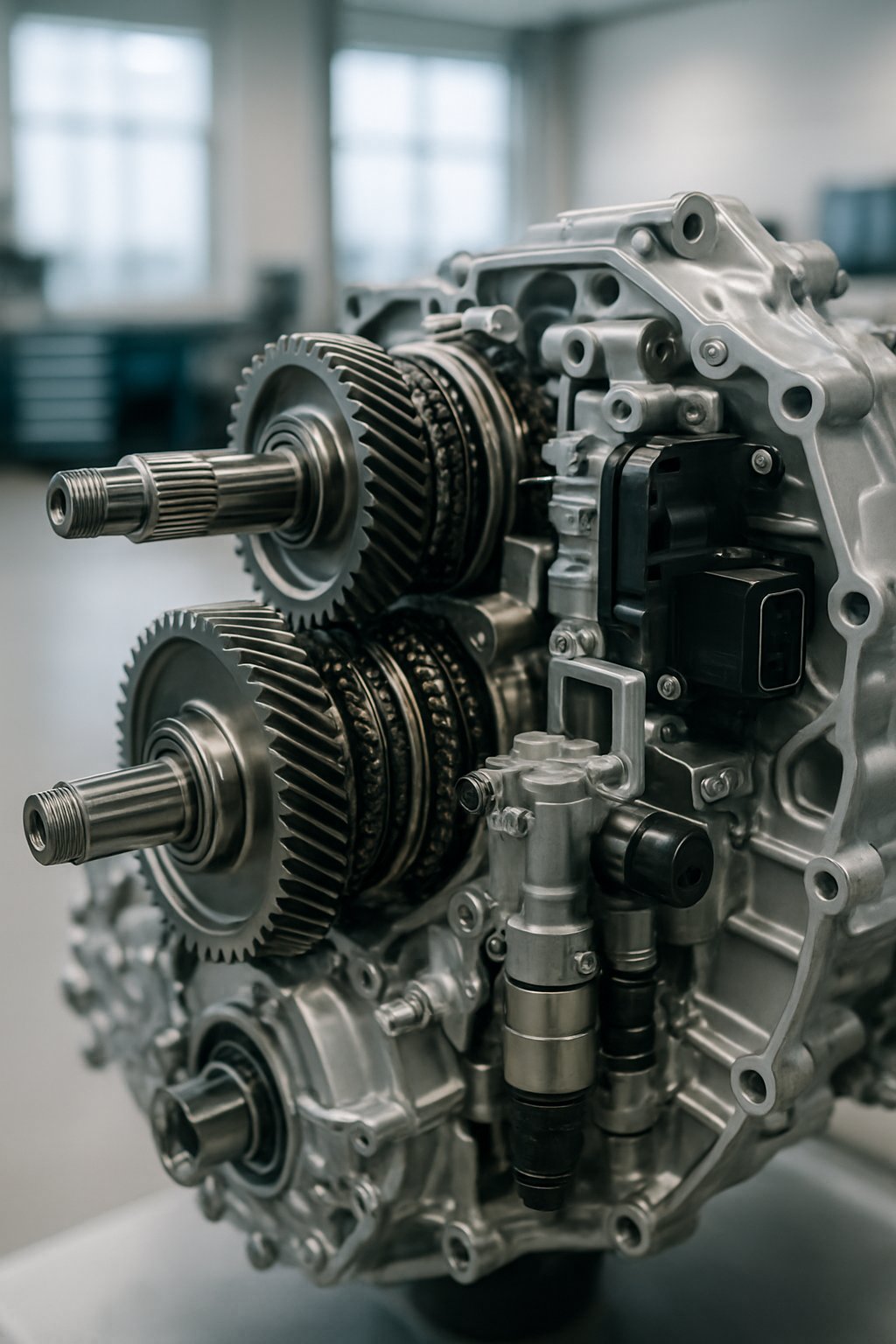
The DSG gearbox is a type of transmission that blends the features of manual and automatic systems. It uses advanced technology to offer fast gear changes and better driving control without the need for a clutch pedal.
DSG Definition and Full Form
DSG stands for Direct Shift Gearbox. It is a type of automatic transmission that controls gear changes electronically. This gearbox uses two clutches instead of one, which improves shifting speed and smoothness.
The term “Direct Shift” refers to how the gearbox shifts gears directly using two sets of gears working together. This design allows one gear to be engaged while the next gear is already pre-selected, leading to faster gear changes than traditional automatics.
Direct Shift Gearbox Explained
A Direct Shift Gearbox contains two separate clutches and two sets of gears inside a single housing. One clutch manages odd-numbered gears while the other controls even-numbered gears.
This setup lets the gearbox switch gears quickly by alternating between the two clutches. The system works fully automatically but can also allow manual gear selection if the driver wants more control.
By eliminating the torque converter found in regular automatic transmissions, the DSG gearbox improves fuel efficiency and driving performance. It is commonly found in cars with front-wheel drive or all-wheel drive layouts.
DSG vs. DCT Terminology
DSG and DCT (Dual-Clutch Transmission) often describe the same technology but differ slightly in usage.
DSG is Volkswagen’s brand name for their specific dual-clutch system. It was developed mainly for Volkswagen Group vehicles, including Audi and Skoda.
DCT is the general term for any dual-clutch transmission regardless of manufacturer. It describes the technology of using two clutches for faster, smoother gear changes.
Both DSG and DCT provide similar benefits: faster shifts and better fuel economy compared to single-clutch automatics. However, DSG refers specifically to Volkswagen’s version of this technology.
How DSG Gearboxes Work
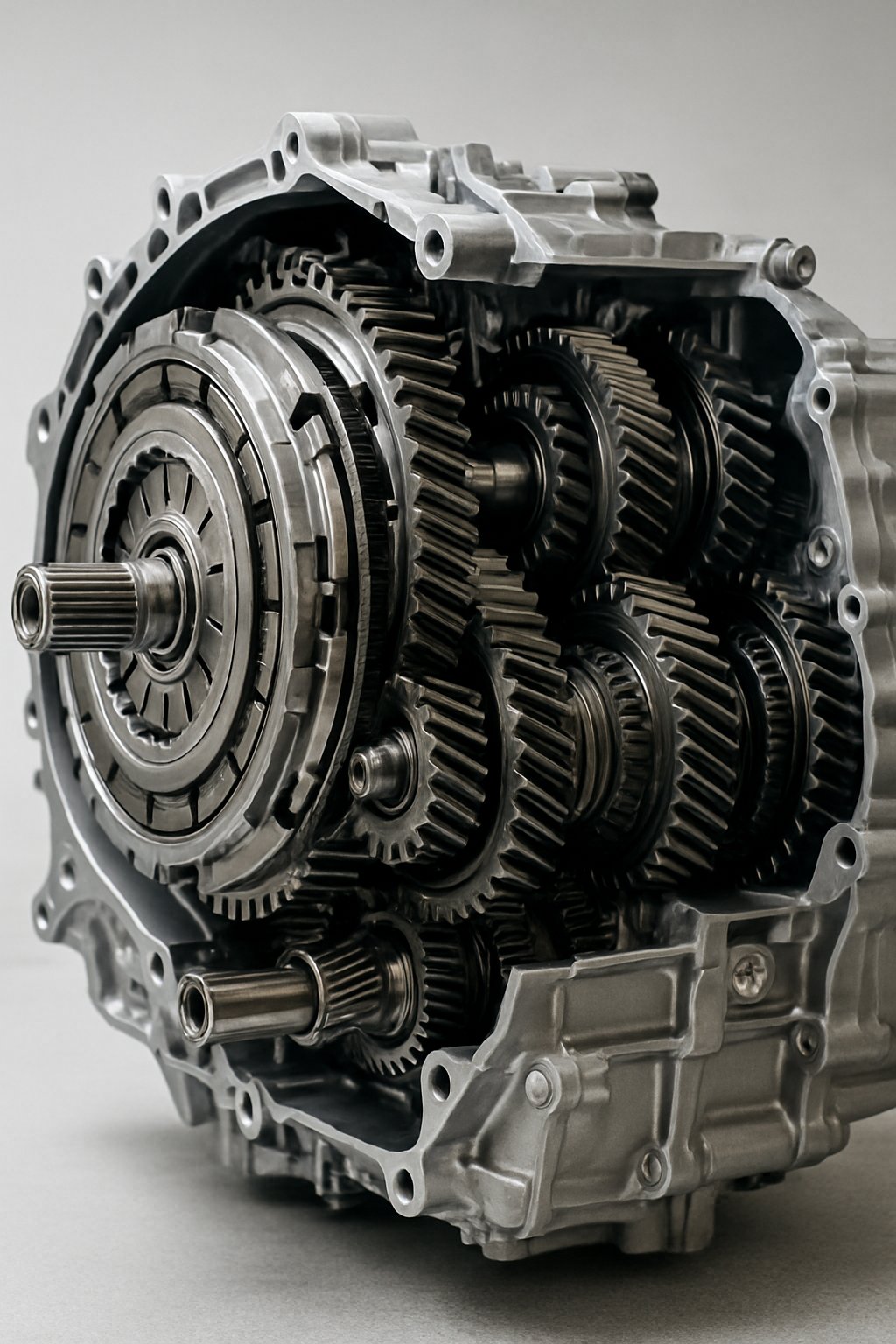
A DSG gearbox uses a unique setup that combines two gearboxes and two clutches in one unit. This design enables smooth and fast gear changes. The system relies on precise electronic control to manage gear shifts automatically, improving performance and efficiency.
Dual-Clutch System Design
The core of a DSG is its dual-clutch system. Instead of a single clutch like in traditional manuals, it uses two clutches arranged side by side. Each clutch operates its own set of gears separately.
One clutch handles odd-numbered gears (1st, 3rd, 5th, etc.), while the other controls even-numbered gears (2nd, 4th, 6th, etc.). This separation allows one set of gears to be engaged while the other is ready to be selected next.
This design eliminates the need for a torque converter, common in automatic gearboxes, helping the DSG respond faster during gear changes. The clutches can be either dry or wet, depending on the model, influencing performance and durability.
Two Gearboxes: Odd and Even-Numbered Gears
Effectively, the DSG gearbox contains two gearboxes enclosed together. One gearbox carries the odd-numbered gears, and the other carries the even-numbered gears. Each has its own clutch, which can engage or disengage independently.
While one clutch holds the gear currently in use, the other pre-selects the next gear. For example, if the car is in 3rd gear (odd), the system pre-selects 4th gear (even) on the second gearbox, making the next shift ready instantly.
This setup reduces the time between gear changes because the system does not need to disengage and engage a single clutch each time. This means faster acceleration and smoother driving, especially during rapid gear changes.
Gear Shifts and Gear Change Process
During operation, when the vehicle needs to shift gears, the DSG disengages one clutch while simultaneously engaging the other. Since the next gear is already pre-selected on the other gearbox, the shift happens almost instantly.
This dual action means there is little to no interruption in power delivery to the wheels. The smooth transition reduces jerkiness and improves fuel efficiency.
The gear change process involves hydraulic actuators supported by a mechatronic unit that manages clutch operation and gear selection precisely. The use of two clutches and gearboxes allows seamless upshifts and downshifts without the delays typical in manual or traditional automatic gearboxes.
Role of Electronic Control Units
The DSG gearbox depends heavily on its electronic control units (ECUs). These computers monitor speed, engine load, and driver input to decide the best time to shift gears.
The ECU controls the clutches and gear selectors using sensors and hydraulic systems, ensuring gear shifts are quick and smooth. It also adjusts clutch pressure to avoid slipping and wear.
By managing the timing and speed of gear changes, the ECU maximizes performance and reduces fuel consumption. It can switch between fully automatic mode and semi-manual mode, where the driver can request gear changes without a clutch pedal.
This integration of electronics and mechanics is essential for the DSG’s fast and efficient operation.
Comparing DSG with Other Transmissions
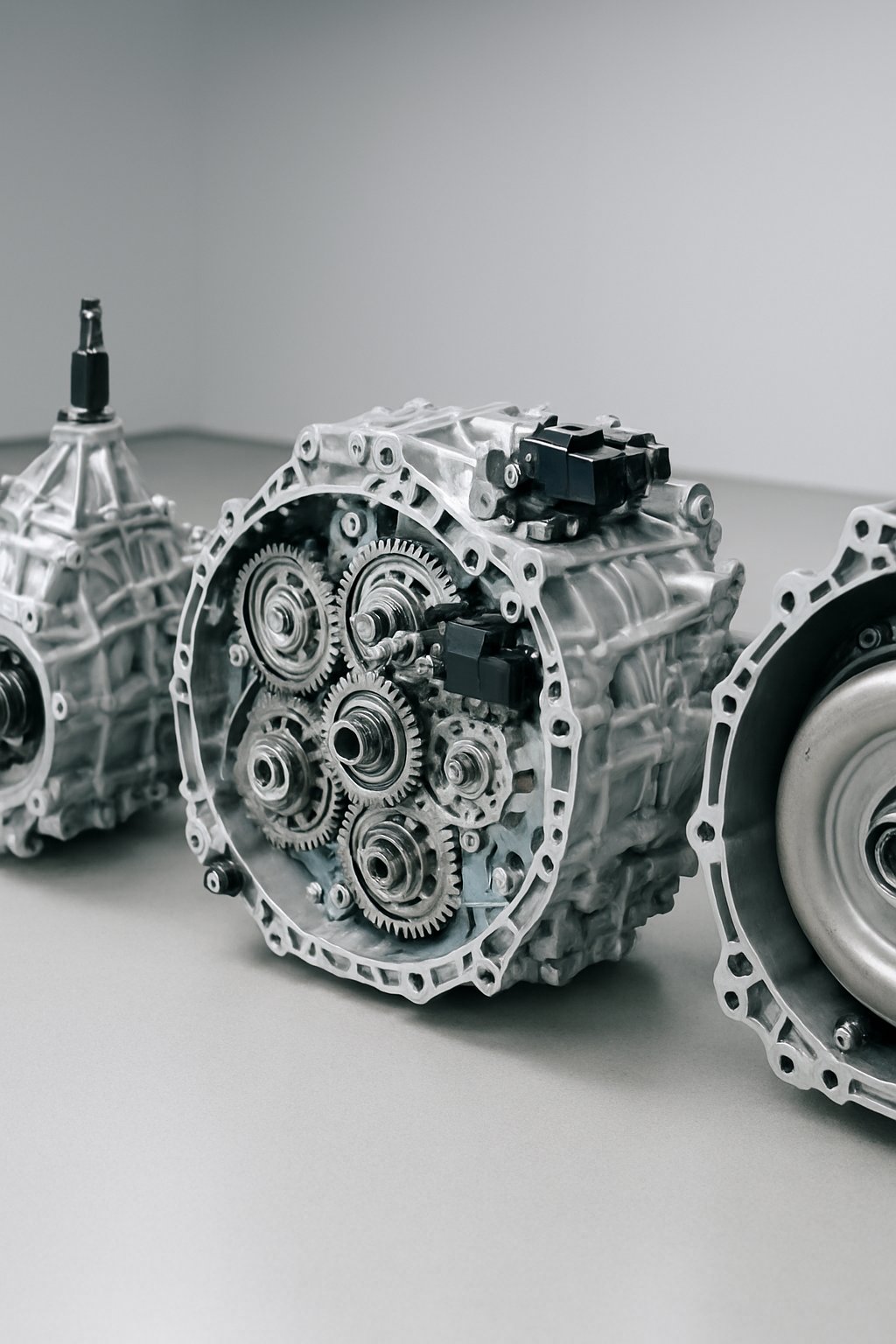
The DSG gearbox offers a unique blend of speed and efficiency by combining features of manual and automatic transmissions. It shifts gears faster and often more smoothly than traditional systems, but its design and operation differ in key ways that affect driving feel and maintenance.
DSG vs. Automatic Transmission
A standard automatic transmission usually relies on a torque converter to smoothly transfer power from the engine to the wheels. This design can cause slower gear changes and slightly reduced fuel efficiency compared to a DSG.
In contrast, DSG uses dual clutches to pre-select the next gear, allowing near-instant shifts without loss of power. This leads to faster acceleration and improved responsiveness. DSG gearboxes also often deliver better fuel economy than classic automatics.
However, DSG systems can be more complex and costly to repair. Traditional automatics tend to be more durable and simpler to maintain, making them popular for everyday use in many vehicles.
DSG vs. Manual Gearbox
A manual gearbox requires the driver to operate a clutch pedal and shift gears manually. This offers full control over gear changes but demands more skill and effort.
DSG combines the control of a manual with the ease of an automatic. It achieves this by using two separate clutches to handle odd and even gears, allowing fast, automated shifting without a clutch pedal.
Compared to manuals, DSG provides smoother gear changes and reduces the risk of stalling. It also allows quicker shifts during sporty driving. On the downside, DSG gearboxes can be more expensive and may require specialized servicing.
DSG and Torque Converter Differences
The torque converter is a fluid coupling device found in most automatic gearboxes. It allows for smooth power transfer and can absorb engine vibrations but often sacrifices shift speed.
DSG gearboxes do not use a torque converter. Instead, they rely on two clutches that work together to engage gears directly. This direct mechanical connection improves shift speed and efficiency.
While torque converters smooth out gear changes, they can cause slight power loss. DSG avoids this by offering sharper, more precise gear changes, which benefits performance and fuel economy but may feel less smooth at very low speeds.
Benefits and Drawbacks of DSG Gearboxes

DSG gearboxes offer fast gear changes and good fuel efficiency, but they also come with some common technical issues. They provide options for manual control and different driving modes. However, cost and reliability can be concerns, especially under certain driving conditions.
Performance and Efficiency Advantages
DSG gearboxes use two clutches to shift gears quickly and smoothly. This means gear changes happen almost instantly, which improves acceleration and driving flow. The faster shifts also help save fuel, making DSG transmissions more efficient than many traditional automatics or manuals.
Because one set of gears is always ready while the other is engaged, the vehicle experiences very little power loss during shifts. This smooth transition is beneficial for both city and highway driving. However, the transmission can be sensitive to heat, especially in heavy traffic or aggressive driving, which can affect performance.
Driving Modes and Manual Shifting Options
Many DSG gearboxes come with selectable driving modes like eco, sport, or comfort. These modes adjust how the transmission shifts gears, tailoring the driving experience. Sport mode, for example, holds gears longer for more power, while eco mode shifts earlier to save fuel.
Drivers can also switch to manual mode to control gear changes themselves using either paddle shifters or the gear lever. This gives more control, similar to a manual gearbox but without the need to operate a clutch pedal. The manual mode suits drivers who want more involvement or need specific gear positioning on hills or winding roads.
Common Problems and Reliability Concerns
DSG gearboxes can be expensive to repair if they fail. Common issues include clutch wear, especially with dry-clutch designs, which are more heat-sensitive. Overheating can activate limp mode, reducing power to protect the transmission but limiting performance.
Some drivers report jerky shifts at low speeds or hesitation when moving off. Regular maintenance, like fluid changes, is critical to keep the system running well. Repairs and part replacements tend to cost more than traditional manuals due to the complex design.
DSG Gearbox Applications Across Brands

DSG gearboxes are widely used in many car models and brands worldwide. They provide fast, smooth gear changes, improving driving comfort and efficiency. Different manufacturers adapt DSG technology to fit their vehicles’ specific needs.
Volkswagen Group and VW Models
Volkswagen Group is the main developer of DSG gearboxes. The technology first appeared in the VW Golf Mk4 R32 in 2003. Since then, it has been used in many Volkswagen models like the Golf, Polo, and Passat.
VW uses different DSG versions depending on the car’s size and engine power. For example, the DQ200 seven-speed DSG with dry clutches fits smaller cars with engines up to 1.6 liters. Larger models with more torque use the DQ250 or DQ381 with wet clutches. These gearboxes offer quick shifts and better fuel economy.
The technology is also found in Volkswagen’s plug-in hybrids, like the Golf GTE, using special DSG versions that combine the electric motor with the gearbox.
Audi, Porsche, and Other Manufacturers
Audi, part of the Volkswagen Group, uses DSG gearboxes under the name S tronic. Audi’s versions typically handle more power and feature dual wet clutch systems. These are found in models like the Audi A3 and the sporty Audi RS3.
Porsche, a pioneer in dual-clutch transmissions since the 1980s, developed technology that influenced later DSG designs. Porsche uses similar dual-clutch gearboxes in models like the 911 and Cayman, though they often call it PDK.
Other premium brands like BMW and Cupra use similar dual-clutch technology but with their own design names. These gearboxes balance performance and smooth driving in sporty models.
Ford, Hyundai, and Global Adoption
Outside Volkswagen Group, other manufacturers have adopted DSG or similar dual-clutch gearboxes to improve efficiency.
Ford uses dual-clutch gearboxes in models like the Fiesta and Focus to offer faster shifts and better fuel economy than traditional automatics.
Hyundai includes dual-clutch transmissions in smaller cars like the Hyundai i30 and Kia Ceed, aiming to offer smooth automatic gear changes with less weight and better efficiency.
Honda and other global brands also use dual-clutch gearboxes, showing the widespread appeal of this technology. While not always called DSG, the principle remains the same: two clutches working together to improve shift speed and driving feel.
Frequently Asked Questions

This section covers how DSG gearboxes differ from traditional automatics, how to drive them, and what sets DSG apart from DCT systems. It also explains what TSI DSG means, points out common 7-speed DSG issues, and shows how to identify the specific DSG model in a car.
What are the differences between DSG and traditional automatic gearboxes?
DSG gearboxes use two clutches, which let them pre-select the next gear for faster and smoother shifts. Traditional automatics usually have a torque converter, which shifts gears using fluid coupling. DSGs are generally quicker in gear changes but can be slightly heavier and sometimes less fuel-efficient.
How should one operate a vehicle with a DSG transmission?
Driving a DSG car is like driving a normal automatic. There is no clutch pedal, and the gearbox handles shifts automatically. The driver usually needs to press the brake to move the gear selector between Park, Reverse, Neutral, and Drive. Some DSG cars offer manual mode with paddle shifters or a gear lever for more control.
Can you explain the distinction between DSG and DCT?
DSG is a brand name for Volkswagen Group’s dual-clutch transmission. DCT stands for dual-clutch transmission and is a general term used by other manufacturers. Both DSG and DCT work on the same dual-clutch system principle, but naming and specific designs vary by brand.
What does TSI DSG mean in the context of vehicle transmissions?
TSI refers to Volkswagen’s turbocharged petrol engine technology. When paired with a DSG gearbox, it means the car combines a direct-shift dual-clutch transmission with a TSI engine. This setup aims to deliver strong performance and efficient power delivery.
What are some common issues associated with 7-speed DSG gearboxes?
Some 7-speed DSG gearboxes may show problems like juddering when starting off, delayed or rough gear shifts, or warning lights triggering limp mode. These issues often happen in older or high-mileage cars and usually require professional servicing or repair.
How can I identify which DSG gearbox model is in my vehicle?
The DSG model can usually be found in the car’s technical documentation or service manual. Sometimes, it’s indicated on a label inside the engine bay or near the transmission. Checking the Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) with a dealer or manufacturer can also reveal the exact DSG model.