How to Change DSG Gearbox Oil and Filter: Step-by-Step Guide
A DSG (Direct Shift Gearbox) needs regular oil and filter changes to keep it shifting smoothly and to prevent premature wear. Changing the DSG gearbox oil and filter every 40,000 miles helps maintain performance and extend the life of the transmission. This service replaces the old fluid, which can lose its protective qualities over time, and installs a fresh filter to keep the system clean.
Many Volkswagen, Audi, Skoda, and SEAT models use the DSG transmission, and while the process is more involved than a standard oil change, it can be done with the right tools, parts, and preparation. The job requires draining the old fluid, replacing the filter, and refilling the gearbox to the correct level while monitoring fluid temperature.
By following a clear step-by-step process and using the correct specifications, anyone with basic mechanical skills can complete this maintenance at home. The upcoming sections explain the purpose of the DSG oil and filter, list the tools and parts needed, provide detailed instructions, and share practical tips to ensure a smooth and successful service.
Understanding DSG Gearbox Oil and Filter Change
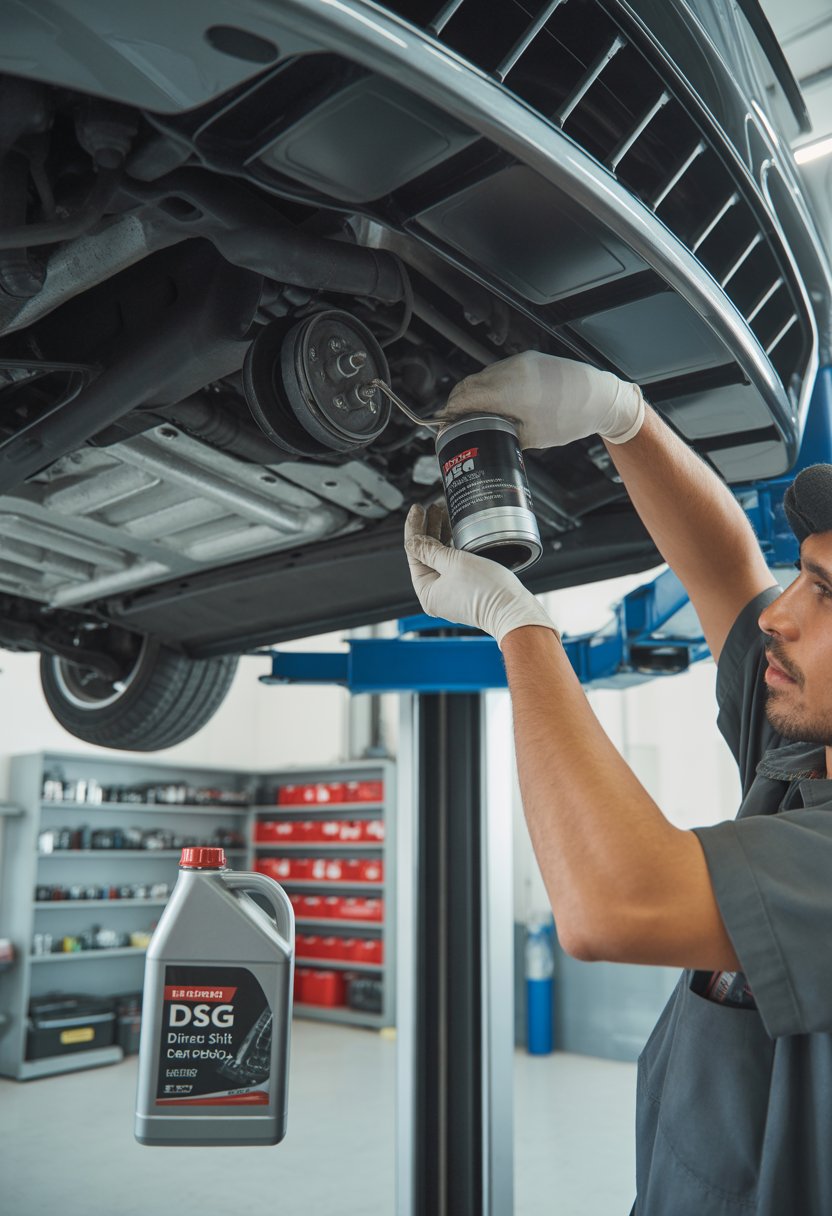

A DSG transmission uses a dual-clutch system that relies on clean, properly lubricated gearbox oil to operate smoothly. The oil also works with the filter to remove debris and maintain correct hydraulic pressure for gear changes. Neglecting this service can lead to rough shifting, overheating, or internal wear.
Why DSG Transmission Oil and Filter Need Regular Changing
DSG gearbox oil lubricates moving parts, cools internal components, and transfers hydraulic pressure for clutch operation. Over time, heat and friction break down the oil’s protective properties.
Small metal particles from clutch wear and gear contact also build up in the fluid. The filter traps these particles, but it can become clogged and reduce oil flow.
When oil loses viscosity or becomes contaminated, the gearbox may shift less smoothly, generate more heat, and wear faster. Regular oil and filter changes help maintain proper lubrication and prevent costly repairs.
Recommended Service Intervals for DSG Gearbox Oil
Most 6-speed wet-clutch DSG transmissions require an oil and filter change every 40,000 miles (about 64,000 km). Some newer models or dry-clutch DSG units may have different schedules, but wet-clutch systems are more sensitive to oil quality.
Following the manufacturer’s maintenance schedule is important because DSG oil works under high pressure and temperature. Even if the vehicle is driven lightly, oil still degrades over time.
In severe driving conditions—such as frequent stop-and-go traffic, towing, or hot climates—oil changes may be needed sooner. Checking the service manual or consulting a qualified technician ensures the correct interval for the specific gearbox type.
Signs Your DSG Gearbox Oil Needs Changing
Drivers may notice slow or jerky gear shifts, especially when starting from a stop. Delayed engagement when selecting drive or reverse can also indicate degraded oil.
Other signs include increased transmission noise, shuddering during acceleration, or a burning smell from overheated fluid. In some cases, the gearbox warning light may appear on the dashboard.
If these symptoms occur before the scheduled service interval, the oil and filter should be inspected. Continuing to drive with worn fluid can accelerate clutch wear and damage internal components, leading to more expensive repairs.
Essential Tools and Parts for DSG Oil and Filter Change
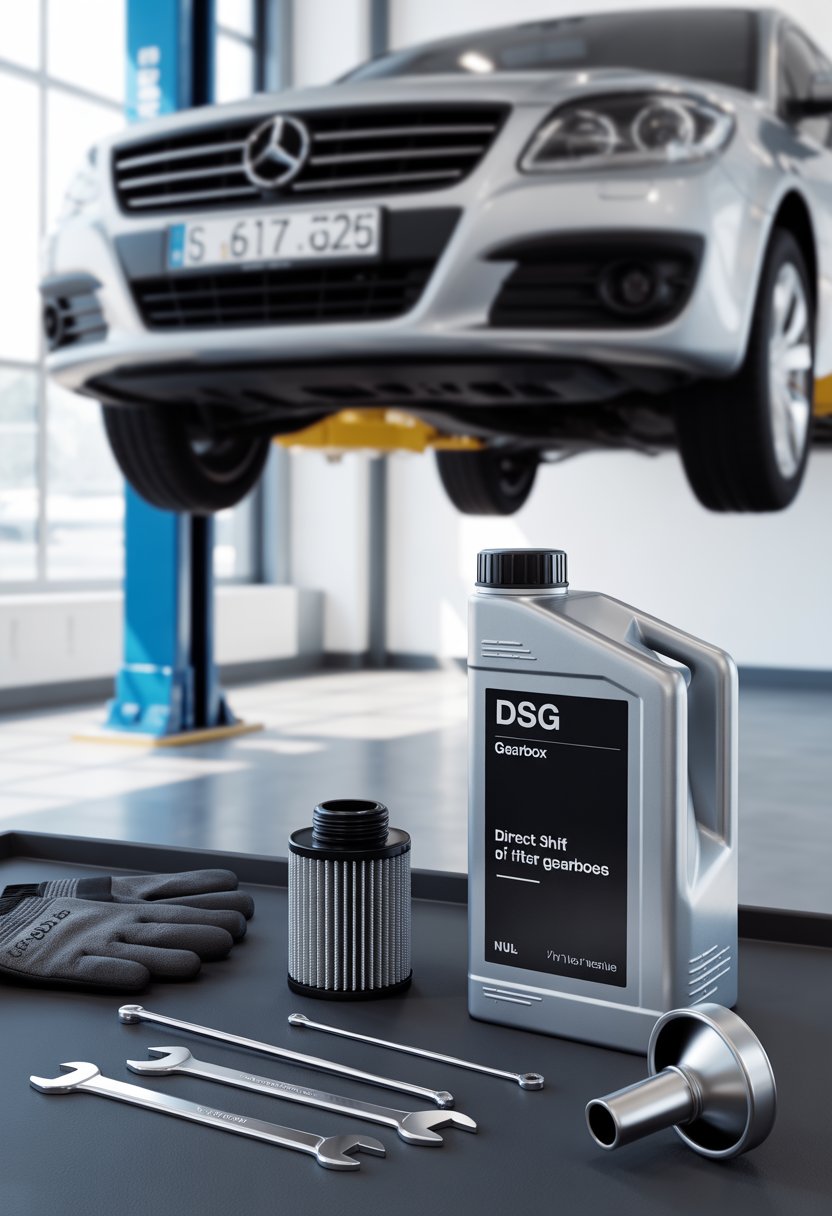

Changing the DSG gearbox oil and filter requires the correct tools, the proper specification oil, and a clean, safe work area. Using the right equipment helps prevent damage to components and ensures the job is completed efficiently.
Required Tools and Equipment
The job needs a mix of standard and vehicle-specific tools. A 24mm socket is required for removing the DSG filter housing. An 8mm Allen socket is used for the overflow tube, and a 14mm Allen socket is needed for the main drain plug.
A torque wrench is essential to tighten bolts to factory specifications, such as 20 Nm for the filter housing and 45 Nm for the drain plug.
A fluid filling system, such as the VAS 6262 or an aftermarket equivalent, helps add gearbox oil through the fill port. A large drain pan is needed to collect about 5–6 liters of used oil.
Other useful items include:
- T20 Torx bit (if airbox removal is needed for access)
- Oil-safe funnel and tubing (for top-fill methods)
- Nitrile gloves and shop rags for cleanliness
- Jack and axle stands or a vehicle lift for safe access underneath
Selecting the Right Gearbox Oil and Filter
DSG gearboxes require specific oil to maintain proper clutch and gear lubrication. Most DQ250 6-speed DSG units use oil meeting VW specification G 052 182 A2. This oil is sold in 1-liter bottles, and a full service usually needs 5.5–6 liters.
The filter should match the gearbox model. For many VW and Audi DSG units, the correct filter is part number 02E 305 051 C and comes with an O-ring seal. Always replace the O-ring to prevent leaks.
Buying OEM or high-quality aftermarket parts ensures correct fit and performance. Cheap or incorrect oil can cause poor shifting and premature wear. Shaking the oil bottles before use helps mix additives evenly.
Preparing Your Workspace
The car must be parked on a level surface with the parking brake engaged. If using a jack, secure the vehicle with axle stands before working underneath.
Lay out all tools and parts within easy reach. Keep the new filter and O-ring in a clean, dust-free area until installation.
Place a large oil drain pan under the transmission before loosening any plugs. Have shop towels ready to wipe up spills. Proper lighting under the car makes it easier to see bolts and connections.
Dispose of used DSG oil at a recycling center or auto parts store that accepts waste fluids. This prevents environmental harm and keeps the workspace clean.
Step-by-Step Process for Changing DSG Gearbox Oil
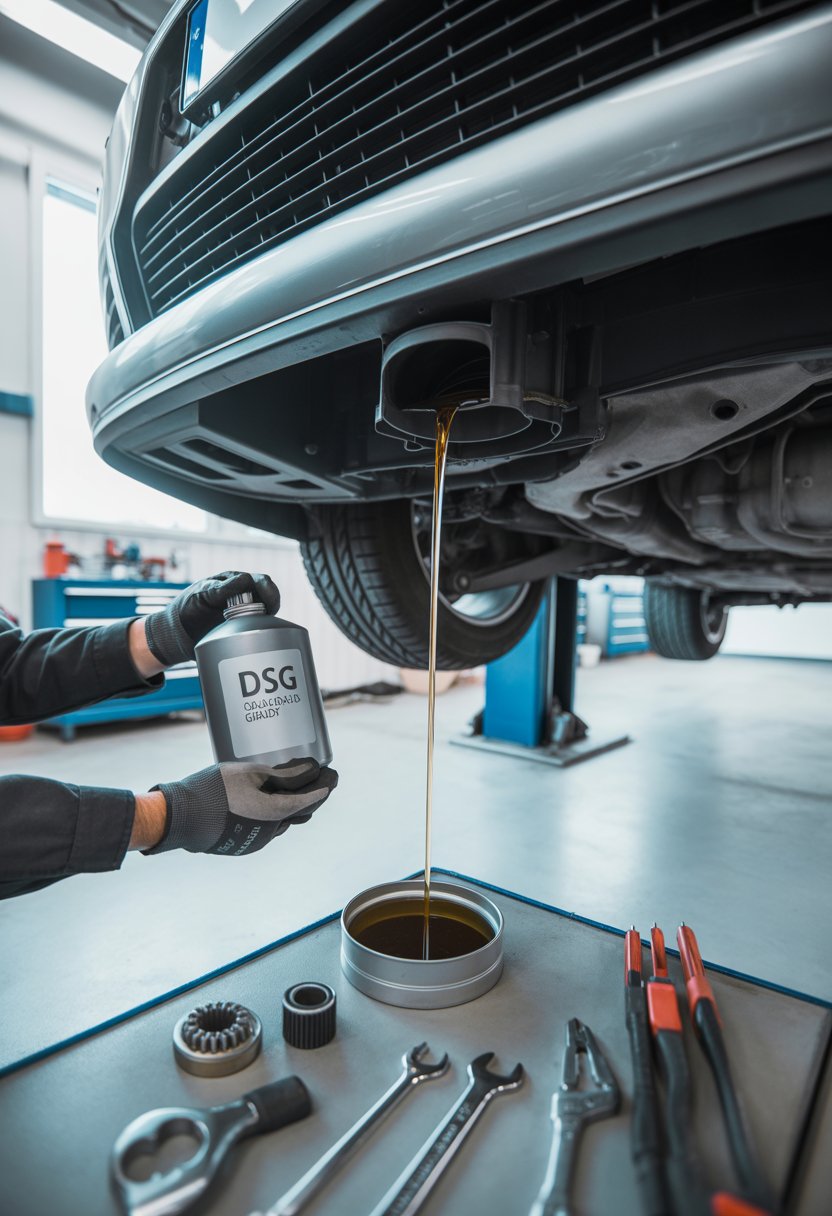

Changing the DSG gearbox oil and filter involves draining the old fluid, replacing the filter, adding the correct amount of new oil, and ensuring the transmission operates within the right parameters. Each stage requires the correct tools, attention to detail, and the use of oil that meets the manufacturer’s specifications.
Draining the Old Gearbox Oil
The vehicle should be parked on a level surface and securely lifted using jack stands or a lift. This ensures safe access to the DSG transmission’s drain plug.
A drain pan is placed directly under the gearbox. The drain plug is then removed using the correct size Allen or socket tool. Oil will begin to flow out immediately.
It is important to let the oil drain completely. This usually takes several minutes. Some DSG units have a plastic overflow tube inside the drain port that must be removed to release all the fluid.
Once drained, the plug and sealing washer should be inspected for wear. If damaged, they must be replaced to prevent leaks after reassembly.
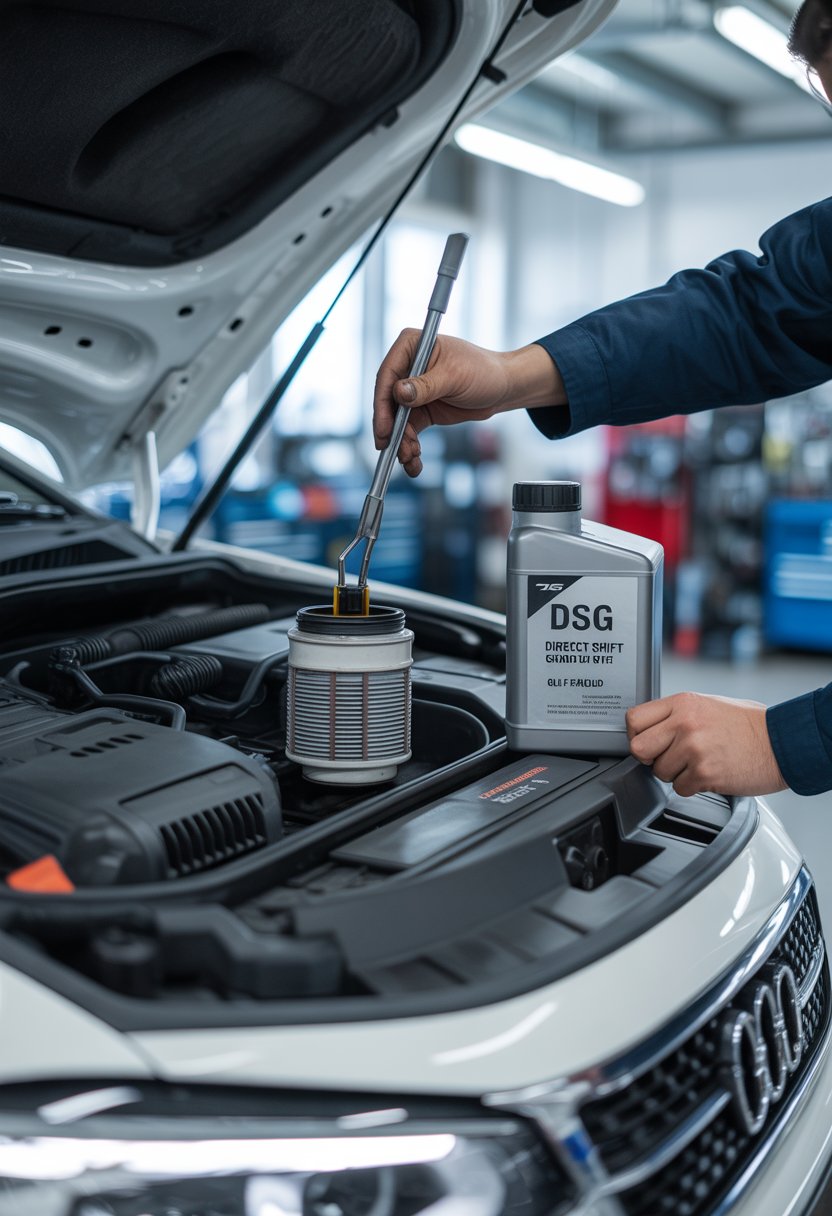
Replacing the DSG Oil Filter
The DSG oil filter housing is often located on top of the gearbox, under the air intake assembly. Removing the airbox and related hoses may be necessary for access.
A socket, often 24mm, is used to unscrew the filter cap. The old filter is removed, and any remaining oil in the housing is allowed to drain back into the gearbox.
The O-ring on the filter cap should always be replaced with a new one. Lightly oiling the O-ring before installation helps it seat properly and prevents damage.
The new filter is inserted, and the cap is threaded on by hand to avoid cross-threading. It is then tightened to the specified torque, often around 20 Nm.
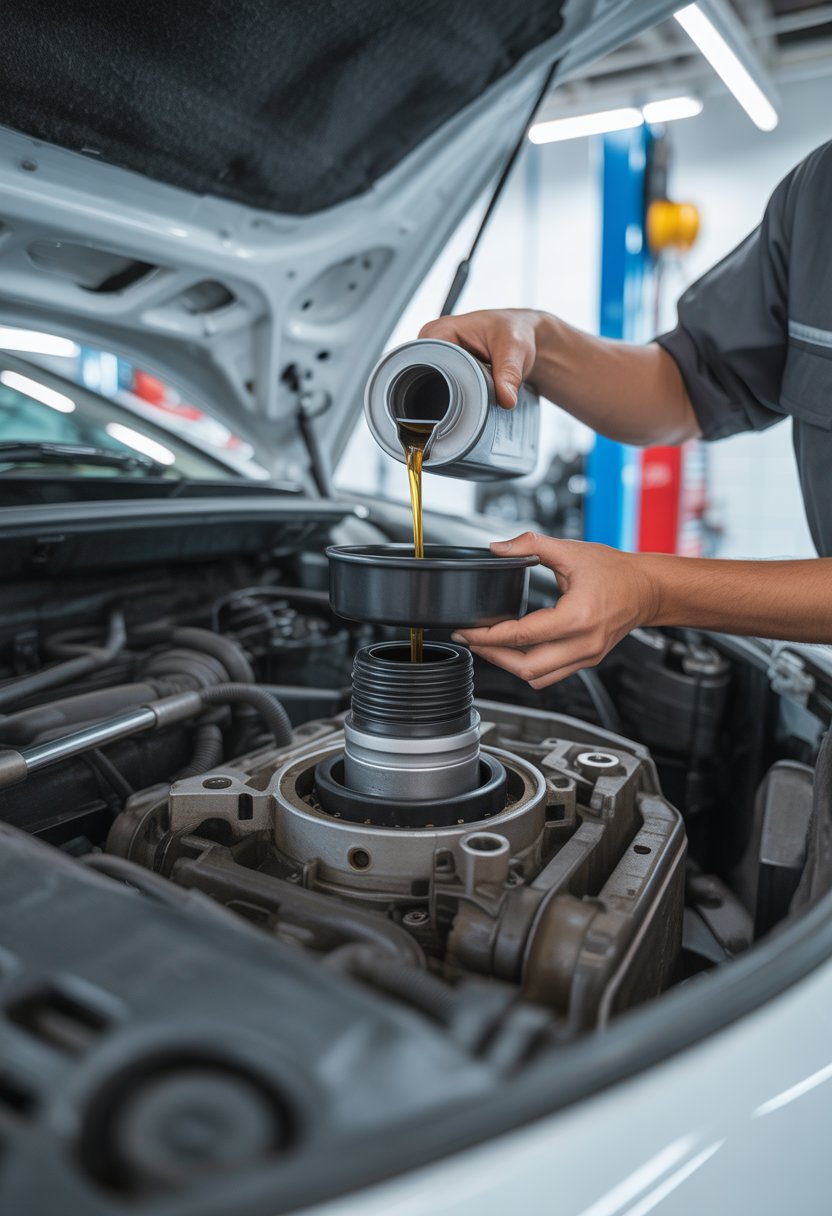
Refilling with New Gearbox Oil
Only DSG-approved gearbox oil should be used, matching the VW specification (for example, VW TL 521 82).
The refill process depends on the gearbox design. Some use a top-fill method through the filter opening, while others require filling from the bottom using a pump.
If filling from the top, the measured amount of oil removed earlier can be used as a guide. Many 6-speed DSG units take around 4.5–5 liters.
After filling, the engine is started, and the transmission is cycled through all gears with the brake applied. This helps distribute oil throughout the system before checking the final level.
Resetting Transmission Adaptations
Modern DSG transmissions use adaptive learning to adjust shift behavior. After an oil change, resetting the adaptations can help the gearbox recalibrate to the fresh fluid.
This is done with a diagnostic tool such as VCDS or OBD-compatible software. The procedure varies by model but usually involves selecting the transmission module and running the adaptation reset function.
Once reset, the vehicle should be driven through a range of speeds and gears. This allows the DSG control unit to relearn shift timing and clutch engagement based on the new oil’s characteristics.
Best Practices for a Successful DSG Oil and Filter Change
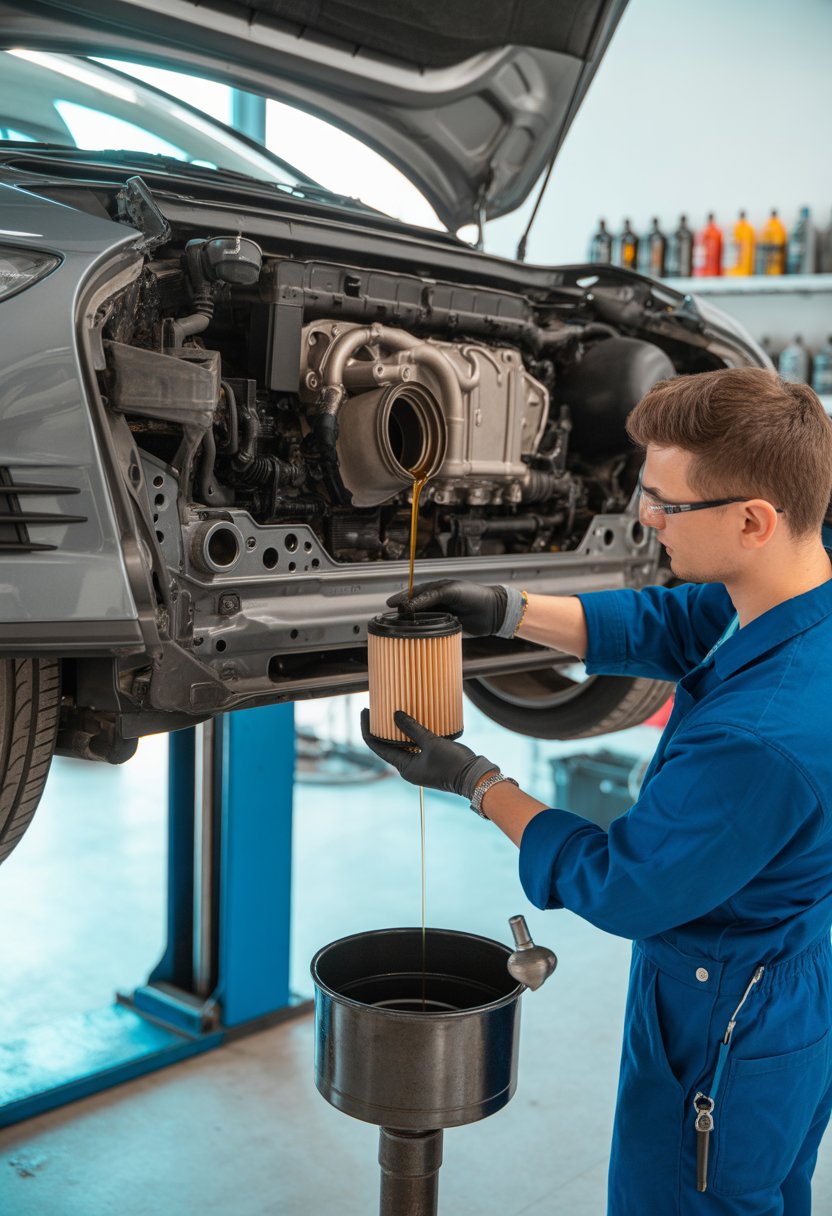

A DSG transmission requires precise servicing to maintain correct lubrication and smooth gear changes. Correct oil level, clean installation practices, and careful post-service checks help prevent premature wear and shifting issues.
Ensuring Proper Oil Level and Temperature
The DSG transmission fluid level depends on both the quantity of oil and its temperature during filling. Most DSG units require the car to be level and the fluid warmed to a specific range, often between 35°C and 45°C.
If the oil is too cold, excess fluid may remain inside, leading to overfilling. If it is too hot, more oil than necessary may drain out, causing underfilling. Both conditions can harm internal components.
Technicians often use a scan tool to monitor fluid temperature. Once the correct temperature is reached, excess oil drains from the level tube until it drips steadily. At this point, the level is correct, and the drain plug can be tightened to the specified torque, such as 33 ft-lb (45 Nm) for many DSG models.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
One common mistake is working with the car on an uneven surface. This can cause incorrect fluid readings and result in improper filling. Always ensure the vehicle is on a stable, level lift or jack stands.
Another error is skipping the replacement of the DSG filter O-ring or reusing worn sealing washers. This can cause leaks under pressure. Always replace these parts with new, approved components.
Contamination is also a risk. Dirt or old oil residue can enter the transmission if tools and parts are not clean. Using a lint-free cloth and ensuring the filter housing is free of debris helps maintain oil cleanliness.
Post-Service Checks and Test Drive
After the oil and filter change, inspect the DSG transmission housing and drain area for any leaks. A short idle period allows the oil to circulate and helps confirm there are no abnormal noises.
During the test drive, check for smooth gear changes in both automatic and manual modes. Pay attention to any hesitation, slipping, or unusual vibration.
It is also important to recheck for leaks after the drive. Even a small drip can lead to fluid loss over time, so tightening any loose fittings immediately is recommended.
Maintenance Tips and Long-Term Care

Keeping a DSG transmission in good condition requires regular fluid changes, careful driving habits, and attention to early signs of wear. Proper oil levels, correct service intervals, and smooth operation checks help prevent costly repairs.
How to Extend the Life of Your DSG Gearbox
Drivers should follow the manufacturer’s service schedule, which often recommends a DSG gearbox oil and filter change every 40,000 miles (64,000 km) for most wet-clutch systems. Skipping this can cause poor shifting and internal wear.
Avoid holding the car on an incline using the throttle. This puts extra strain on the clutches. Use the brake instead.
During stop-and-go traffic, it helps to switch to neutral when stationary for long periods. This reduces clutch heat and wear.
Only use DSG-approved oil that meets the correct VW specification (such as VW TL 52 182). Using the wrong fluid can cause shifting problems and damage the gearbox.
If towing, keep loads within the vehicle’s rated limits. Heavy loads increase gearbox temperature and stress.
Monitoring Gearbox Performance After Service
After a DSG oil and filter change, drivers should check for smooth gear changes and consistent acceleration. Any hesitation, jerking, or slipping may indicate low oil level or incorrect installation of parts.
It is important to monitor for oil leaks around the drain plug, filter housing, and fill port. Even small leaks can lower fluid levels and affect lubrication.
A temperature scan with a diagnostic tool can confirm the gearbox oil is operating within the normal range, typically 35°C–45°C during service checks.
Listening for unusual noises, such as whining or clunking, can help detect early mechanical issues. Addressing these quickly may prevent further damage.
If problems appear soon after service, the vehicle should be inspected by a qualified technician to verify fluid levels, torque settings, and component condition.
Frequently Asked Questions

DSG transmissions require specific maintenance steps, including oil and filter changes at set mileage intervals. The process involves using the correct fluid type, following a precise drain and refill method, and ensuring the system operates at the correct temperature during filling.
What is the recommended interval for changing the oil and filter in a DSG transmission?
Most 6-speed DSG gearboxes require an oil and filter change every 40,000 miles or every 4 years, whichever comes first. Some newer 7-speed dry-clutch DSG units may have different requirements, so it is important to check the vehicle’s service manual.
Can I change the DSG transmission oil and filter myself, and what tools are required?
Yes, skilled DIY mechanics can perform this service. Common tools include a 24mm socket, torque wrench, oil drain pan, DSG oil filling tool, and an 8mm hex key for the overflow tube. A vehicle lift or jack stands are also needed for safe access to the transmission.
What type of oil should be used for a DSG gearbox, and does it vary by vehicle model?
Use only oil that meets the VW DSG specification (commonly VW TL 52 182). The exact fluid type can vary between DSG models, so the part number or specification in the owner’s manual should be confirmed before purchase. Using the wrong oil can cause shifting issues or damage.
What are the steps involved in draining and refilling DSG transmission oil?
The process typically involves removing the filter housing, draining oil through the overflow tube, replacing the filter, and refilling with the correct amount of DSG oil. The gearbox must be at the correct temperature—usually 35°C to 45°C—before final leveling and sealing.
How do you reset the service indicator after changing the DSG oil and filter?
On many vehicles, the reset is done through the infotainment system or by using a diagnostic tool such as VCDS or OBDeleven. The reset process varies by model, so following the manufacturer’s instructions is essential.
Are there any common issues to watch out for when changing the oil and filter in a DSG gearbox?
Common issues include overfilling or underfilling the transmission, not tightening bolts to the specified torque, and working with oil that is too hot or too cold. Using incorrect fluid or skipping the temperature check can cause poor shifting or transmission wear.


![2006 Volkswagen Jetta Jerks When Taking Off [Fix It Now!]](https://volkswagenbuddy.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/2006-volkswagen-jetta-jerks-when-taking-off-fix-it-now_4510-768x531.jpg)


![2011 Volkswagen Jetta Ignition Switch Off [Fixed]](https://volkswagenbuddy.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/2011-volkswagen-jetta-ignition-switch-off-fixed_4457-768x531.jpg)